
Comic books have been an especially reliable source of material for Hollywood these days. Marvel and DC have been in a heated battle for box office supremacy, with their collection of heroes and rogues turning into the matinee idols of our current modern age. And sure, there is a lot to draw from given the countless amount of stories that have been written for the comic medium for nearly a century now. It wasn’t until recently, when Marvel took upon developing their cinematic universe, that comic book movies resulted in a business model that has generated billions of dollars in grosses. Now, comic book movies are mainstream, with even the most obscure of comic characters like Hawkeye or Rocket Raccoon become household names. The downside of this is that comic book movies tend to become formulaic as a result; with studios wanting to take fewer risks as they invest more and more money into these potential blockbusters. What this leads to is an increasing disconnect between what we see on the big screen and what we usually find on the page from the original source comics. Comic books live by their own set of standards, and it’s usually a lot more open to challenging and evocative stories and characters. There’s usually a lot more violence, sex, and profanity found in even some of your standard trade comics, and avenues taken by some of the most popular charcters that you wouldn’t normally see them do in the movies. Comic fans usually embrace these riskier stories, and they hold the film adaptations to a higher standard as a result. Filmmakers find many interesting ways to work around the risks of adapting some of the more problematic comics by making movies more inspired by the comic books instead of making straightforward translations; Marvel’s recent Civil War is a perfect example of this. But, when the source comic is as highly acclaimed and renowned as a single piece, as many graphic novels are, the liberties taken tend to become more of a problem.
There is a significant difference between what we see as a comic book and as a graphic novel. Comic books are short form stories, sometimes tied together in a serial fashion, meant to be consumed by the audience as quick, action packed entertainment. Graphic novels on the other hand are developed as deeper, long form stories that are often about headier subjects. Essentially, they are novels told through comic strips. Many of the most beloved graphic novels have taken on stories that you would never see on you average comic book stand, such as Art Spiegelman’s Maus, which re-imagines the horrors of the Holocaust with Nazi cats and Jewish mice; or Marjane Satrapi’s Persepolis, which portrays an autobiographical tale of the author’s coming of age in Iran in the aftermath of the Islamic Revolution. But perhaps the most prolific graphic novelist of all time is English writer Alan Moore. Praised for his often revolutionary and provocative style, Moore’s body of work has been a huge influence of the medium as a whole. Moore’s heyday in comic writing was in the 1980’s, where he not only excelled with his own original work, but also crafted some of the most celebrated stories ever for icons such as Batman (The Killing Joke) and Superman (For the Man Who Has Everything). His more political works, however, are the novels he’s best known for, such as V for Vendetta. Naturally, with a body of work as celebrated as his, it was inevitable that Hollywood would come calling. What is interesting about Moore’s approach to film adaptations of his own work is that he is both the most accommodating and the least cooperative of authors. He permits filmmakers to adapt his work, but he always refuses to take part in their making, even refusing any screen credit. This leaves the people responsible for bringing his work to life with the extra responsibility of doing it justice because they have to work without the guidance and approval of Moore himself. And perhaps the film adaptation that presented the hardest challenge to date was of Moore’s iconic 12-part behemoth, Watchmen (2009).

“We are all puppets, Laurie. I’m just the puppet who can see the strings.”
The creation of a Watchmen movie was no easy feat. Developed for years after the publication of Moore’s novel, Watchmen saw many interested parties come and go. Even Terry Gilliam of Monty Python and Time Bandits fame seriously considered adapting the comic, until he abandoned it after famously stating that he thought that the novel was un-filmable. Some serious consideration of an epic TV miniseries on one of the cable networks was also considered until eventually Warner Brothers and DC comics (the publisher of Watchmen) landed on a screen adaptation that they were pleased with. Up until this point, screen adaptations of Moore’s novels had been mixed; from good (From Hell), to mediocre (the Wachowski’s V for Vendetta), to just outright bad (The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen). But critical praise for DC’s The Dark Knight (2008), which was heavily inspired by The Killing Joke in it’s portrayal of the Joker, convinced Warner Brothers to take the risk of adapting Alan Moore’s epic. There was only one crucial issue; who would they get to commit to such an undertaking. They found their director in Zack Snyder, who had just recently received raves for his work adapting another famous graphic novel, Frank Miller’s 300, with almost obsessive faithfulness to the original comic. By giving an exact page to screen translation, and done in an economical way (filmed against green screens with CGI rendered environments), Snyder had gained the confidence of studio brass with his work on 300, and it was believed that his same style of film-making would carry Watchmen through to the end. But, being faithful visually to the graphic novel is much different than being faithful to it as a narrative. What resulted was a mixed bag of a movie where some things worked and a lot of other stuff just didn’t. You would think it would be easy to just carry over the comic pages like a storyboard for a movie, but adaptations are more complex than that, and the movie Watchmen provides an interesting examination into how such a translation can work.

“This city is afraid of me… I’ve see its true face.”
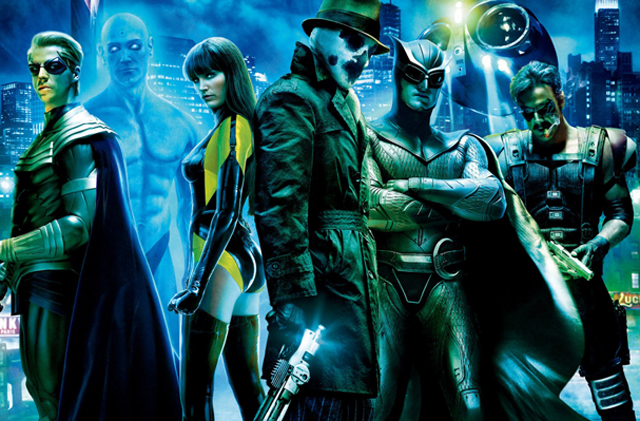
The big problem with adapting a novel like Watchmen is just the overwhelming mass of story. Watchmen was published in 12 separate issues over a year between 1986-87, and then compiled together later as a complete book. And each individual issue has enough story to fill an entire hour worth of screen-time. The story covers much of the themes that has informed most of Alan Moore’s work, which is the deconstruction of the super hero mythos, and what it means to be a hero, and where violence is justified for the greater good of humanity. Watchmen is the most overt statement made by Moore about all these issues, and it’s done with quite a compelling story. The novel let’s us follow different generation of masked vigilantes known as the “Watchmen,” whose heydays have long passed them by and are now working outside of the law for what they believe is for the best of society. The only problem is that their methods are increasingly problematic and do more harm than good, making them social pariahs. The book takes it’s title from the classic Latin phrase, “Quis cutodiet ipsos custodes?” or “Who watches the Watchmen?” It’s a story that calls into question where authority lies, and what do we do when power is unchecked. This is reflected in varying degrees through the flawed characters within the story; the by the book Night Owl, the emotionally broken Silk Spectre, the autocratic Ozymandias, the nihilistic Rorschach, the manic Comedian, and the ethereal Dr. Manhattan. Each of these characters is brought to moral crossroads through the actions they take and the novel does an exceptional job of devoting enough time to understanding who these characters are and what forces both external and internal made them who they are. It’s an exploration of personal and societal dramas that you can’t possibly work entirely into a two to three hour run-time without losing a lot in translation.
I think what plagued the Watchmen movie the most was the fact that it was limited by the confines of cinema. Even with a nearly three hour run time, Watchmen still feels like it just never breaks past the surface. It’s presenting the story, but it never delves any deeper. A lot of the story’s themes had to be streamlined and character moments dropped in favor of more action oriented scenes, which studios tend to value more. As a result, we get a movie that has the look of Alan Moore’s Watchmen, but doesn’t have the same emotional impact, or is as thought-provoking. Some of the edits were understandable, like the comic within the comic Tales of the Black Freighter, which was meant to serve as a parallel fable to underline the psyche of some of what the main characters were going through. You lose some of the introspection without the Black Freighter, but you gain better pacing as a result. Other things cut from the story prove far more problematic, especially the look into the history of the Watchmen. We learn so little about the founding members, and the ones we do meet, including the original Night Owl and Silk Spectre, are so ill-defined that they are no where near as interesting as they are in the comics. This makes one of the novel’s most shocking moments, the murder of Hollis Mason (the first Night Owl) feel sadly weak in the film, because we are so little invested in his story. The film’s socio-political message also gets short-changed in the translation, with Cold War politics taking a back seat most of the time, and questions of misuses of authority becoming less important than watching the main characters kick ass throughout the movie. That, in of itself, is the biggest insult to Alan Moore’s story, because it misses the point of how the people behind the masks are imperfect people and that their judgments are just as flawed as anyone else’s, making their authority all the more problematic. When you take those same characters and given them choreographed fight scenes that make them look cool, you’ve kinda lost the narrative.
“I didn’t mind being the smartest man in the world. I just wish it wasn’t this one.”
Not everything about this movie is a failure though. You can tell that the filmmakers do have an appreciation for the novel, and the faithful adherence to the symbols and iconic images within the novel help to make it at least recognizable as an adaptation of the story. Can’t say the same about anything in The League of Extraordinary Gentelmen (2003). Where the movie also succeeds surprisingly well is in the cast, at least for the most part. In particular, the movie does deserve credit for it’s perfect casting of Rorschach. Character actor Jackie Earle Haley looks like he was born to play the role, and he takes full command of every scene he is in. His Rorschach is Moore’s creation come to life in every way, complete with the harsh raspy voice and volatile personality. The iconic mask is also really well executed in the movie, with the inkblot shape constantly changing form throughout the movie. But the biggest surprise is how well the movie portrays Dr. Manhattan. The blue skinned, god-like super being known as Dr. Manhattan may have been the reason why other filmmakers abandoned the project, because he is such a difficult character to translate to the screen. The comic even differentiates him from the others by making his speech bubble unique in appearance. Casting actor Billy Crudup in the role may have been an unusual choice, but with a calm, scientific tone of voice, his performance actually works amazingly well. I’ve always wondered what Dr. Manhattan would sound like, and Crudup’s understated delivery just feels right. A person with unlimited power would speak in that matter of fact, reserved kind of way. The motion capture animation of the character also is some of the movie’s best effects work. Patrick Wilson and Malin Akerman are serviceable as Night Owl and Silk Spectre respectively, but nothing special. Jeffrey Dean Morgan also shines in his brief moments as The Comedian. If there is a disappointment at all in the cast, it’s Matthew Goode as Ozymandias, who just feels flat and uninterested as the arrogant antagonist of the story.
The movie and the book also have the glaring difference of very contrasting ideas about how to use the visuals to tell their story. Zack Snyder has his many problems as a storyteller, but no one can take away his status as a strong filmmaker. He is indeed capable of delivering some beautifully composed images in his films, and he does have a strong grasp on how to best use extensive visual effects in his movies. However, he also has the reputation of putting too much emphasis on visuals and not enough in the story, making the former feel more hollow as a result. His direction works best with something like 300 (2007), which is a story made for the sole purpose of showing off the visuals and little more. Watchmen on the other hand puts much more emphasis on the story. While artist Dave Gibbons does provide some amazing visuals in the story, like Dr. Manhattan’s clockwork tower on Mars or the Comedian’s bloody demise, his artwork is much more in the service of Moore’s text and less meant to be it’s own thing. Most of Watchmen‘s panels look no more different than your average comic, and that’s intentional. Moore and Gibbons were making a critique of the super hero genre made within the same style. Snyder dispenses with this idea and flourishes his film with his own excessive style, which sometimes works and sometimes doesn’t. Dr. Manhattan’s rebirth is adequately realized on screen in a stunning, epic moment, and so is the realization of his tower. Where the movie does loose some luster is in the depiction of Ozymandias’ fortress in the Antarctic. What should have been a stunning contrast between the warm glow of the inside of the fortress and the harsh coldness outside is unfortunately lost through Zack Snyder’s muted color palette. It’s the point in the movie that felt the most lacking to me compared with what was on the page, and considering that this is where the film’s climax takes place, it increases the unsatisfactory response to the movie as a whole. Was Zack Snyder the wrong choice of director? Well, he wasn’t a great choice, but considering how few others would even attempt this adaptation, I suppose he’s the best that this movie could’ve hoped for.

“What happened to the American Dream? It came true! You’re lookin’ at it.”
What the movie Watchmen shows us is that even something that seems destined for the silver screen in a visual medium like comics and graphic novels doesn’t always guarantee a successful adaptation. In many ways, graphic novels are even harder to translate because the visual realization of the story is already there, making it harder for a movie to live up to that. Alan Moore’s magnum opus is celebrated both as a critique of the super hero genre, and as a perfect representation of the genre itself. It’s harrowing as much as it is provocative, and it has iconic characters that anyone working in the comic medium would love to have for their own. In it’s thirty years, Watchmen has remained a high water mark in its field and still to this day is one of the best-selling graphic novels of all time. I don’t think any movie could ever have come close to capturing what Alan Moore and Dave Gibbons captured on the page. The movie exists purely as an example of how even the most earnest of adaptations can fail to capture the same kind of impact. Was it necessary? Well, you couldn’t expect for DC and Warner Bros. to just sit on the property. The fact that Watchmen is not an incomprehensible mess overall is I guess a sign of some accomplishment. It did nail some of the characterizations, and the fact that so much work went into at least preserving the imagery of what was on the page is worth something. Much like Ozymandias, Zack Snyder took the unenviable burden of taking a job that would result in nothing but a harsh response, so that no one else would have to get their hands bloody in the aftermath. He does add some nice new flourishes, including an outstanding opening credits sequence, but of his many other choices just seemed contradictory to what the story actually needed. Graphic novels are by no means untouchable as sources for film adaptations, but the pressure to do them justice is almost always never worth the risk. As Watchmen shows us, sometimes a story can be fully realized before Hollywood can ever get it’s hands on it, and any other attempt at it will always have to live up to a different standard.

“Rorschach’s Journal: October 12th, 1985. Tonight, a comedian died in New York.”